Deep Learning
Transfer Learning
Transfer learning is dedicated to transfer the knowledge gained from one task to solving other related problems instead of learning from scratch. In the field of data representation, an assumption is that the training and future data must be in the same feature space and have the same distribution (actualy they are). In practice, transfer learning has been applied in model initialization whose parameters are shared by different applications like classification, detection, recognition and regression.
LSTM
This excellent post makes me give up writing.
Networks & Architectures
CNN Networks
Dilated convolution (空洞卷积,扩张卷积)
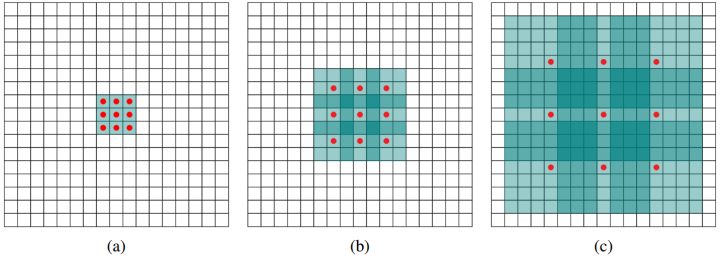 上图(a)(b)(c)分别是3x3的1-dilated, 2-dilated, 4-dilated conv. Dilated conv设计的目的是不会增加参数的数量的同时增加感受野. 尤其是将(a)(b)(c)级联起来之后,感受野由3x3增加到7x7,再增加到15x15.
上图(a)(b)(c)分别是3x3的1-dilated, 2-dilated, 4-dilated conv. Dilated conv设计的目的是不会增加参数的数量的同时增加感受野. 尤其是将(a)(b)(c)级联起来之后,感受野由3x3增加到7x7,再增加到15x15.
Deconvolution (反卷积)
考虑一个4x4的feature map, 经过一个padding 0, stride 1, 3x3的卷积核后变成2x2的feature map, 卷积操作的矩阵运算表达形式为 \(\mathbf{y}_{4\times1}=\mathbf{C}_{4\times16} \mathbf{x}_{16\times1}\). 卷积矩阵\(\mathbf{C}\)的表达式如下:
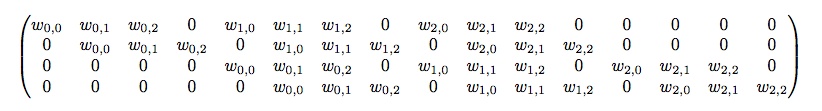
反卷积数学上其实就是卷积矩阵的转置, 反卷积操作可以写为\(\mathbf{x}_{16\times1}=\mathbf{C}^T_{16\times4} \mathbf{y}_{4\times1}\). 所以,反卷积更好的叫法是转置卷积.
Unpooling
Pooling vs. unpooling in figure below.
How to compute receptive field?
A guide to receptive field arithmetic for Convolutional Neural Networks
Loss
focal loss [2]
When approaching the final stage of training, the network is able to handle most of the training cases except for the hard negatives (e.g. those are misclassified). However, the loss caused by the rare hard negatives may be small-valued compared to that caused by well-classified easy ones due to the imbalance in amount. In this way, the easy examples, contributing to the majority of the loss, diminate the gradient and thus mislead training.
Focal loss is defined as
\[\alpha (1-p)^\gamma loss,\]where \(p\) is the quality of being well classified, \(\gamma \geq 0\) is called focusing parameter and \(\alpha \in [0, 1]\) is weighting factor. The factoring term \((1-p)^\gamma\) down-weights the loss caused by easy examples (\(p \approx 1\)) that have been classified good enough. This in turn increases the importance of correcting misclassified examples (\(p << 1\)).
Visualization
MDS (multi-dimensional scaling) tends to preserve the global structure whereas T-SNE tends to retain the local structure.
Platform
Reference
[1] A Survey on Transfer Learning
[2] Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection